The most
effective extinguishing agents for fuel, apolar solvents and plastics
fires are special extinguishing foams which form a water film on the
surface of the burning liquid (Aqueous Film Forming Foams, AFFF).
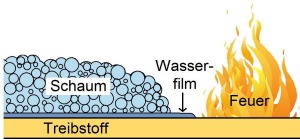 (will be translated, soon)
- It allows easier and thus faster gliding of the foam on the
surface of the burning liquid, and thus a faster extinguishing success
and also a larger application radius.
- The increased flowability of the foam on the water film
promotes the self healing of the foam surface during injuries, e.g. by
falling pieces of debris or objects.
- The water film acts as an additional barrier on the burning
material and, as a steam barrier, reduces the flow of combustible gases
into the gaseous firing zone.
- Due to the large heat of evaporation of water, the
spreading film cools the burning liquid and thus lowers its vapor
pressure.
The ability to form such a water film is conferred to currently
available AFFF by poly- or perfluorinated surfactants (PFS), which are
not degraded in nature (persistence), accumulate in the ecosystem
(bioaccumulation) and are suspected of possess toxic effects. A number
of AFFF applications have led to contamination of soil and groundwater.
Partly, he drinking water abstraction had to be suspended in these
regions.
For these
reasons, the use of the previously frequently used surfactant
perfluorooctylsulfonate (PFOS) in AFFF in the EU was banned and PFOS
was replaced by chemically similar substances, so-called fluoroelomers.
However, these substitutes are still fluorinated
and by far also not safe.
It is therefore
imperative to explore new AFFFs which are complete fluorine free,
environmentally friendly and non-toxic, but at the same time have the
necessary properties; i.e. in
particular extremely low surface and interfacial tensions of their
aqueous solutions.
|
 (will be translated, soon)
(will be translated, soon)